AST 到 字节码
目录
相关位置文件
-
Python/compile.c
-
Python/pythonrun.c
-
Python/symtable.c
-
Include/symtable.h
-
Python/ast_opt.c
我们来尝试从之前的 语法树 中生成对应的字节码
前面提到过的 pythonrun 的调用栈如下
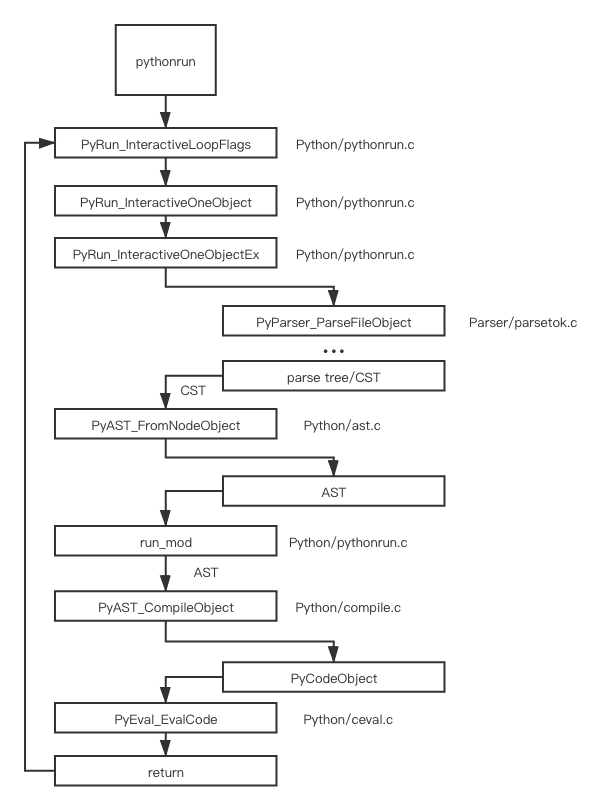
这次关注的是 PyAST_CompileObject 这个函数
PyCodeObject *
PyAST_CompileObject(mod_ty mod, PyObject *filename, PyCompilerFlags *flags,
int optimize, PyArena *arena)
{
struct compiler c;
PyCodeObject *co = NULL;
PyCompilerFlags local_flags;
int merged;
// ... 忽略 ...
if (!_PyAST_Optimize(mod, arena, c.c_optimize)) {
goto finally;
}
c.c_st = PySymtable_BuildObject(mod, filename, c.c_future);
if (c.c_st == NULL) {
if (!PyErr_Occurred())
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_SystemError, "no symtable");
goto finally;
}
co = compiler_mod(&c, mod);
finally:
compiler_free(&c);
assert(co || PyErr_Occurred());
return co;
}
optimize
_PyAST_Optimize 会针对AST做一些优化, 比如常量折叠
static int
fold_binop(expr_ty node, PyArena *arena, int optimize)
{
expr_ty lhs, rhs;
lhs = node->v.BinOp.left;
rhs = node->v.BinOp.right;
if (lhs->kind != Constant_kind || rhs->kind != Constant_kind) {
return 1;
}
PyObject *lv = lhs->v.Constant.value;
PyObject *rv = rhs->v.Constant.value;
PyObject *newval;
switch (node->v.BinOp.op) {
case Add:
newval = PyNumber_Add(lv, rv);
break;
case Sub:
newval = PyNumber_Subtract(lv, rv);
break;
case Mult:
newval = safe_multiply(lv, rv);
break;
case Div:
newval = PyNumber_TrueDivide(lv, rv);
break;
case FloorDiv:
newval = PyNumber_FloorDivide(lv, rv);
break;
case Mod:
newval = safe_mod(lv, rv);
break;
case Pow:
newval = safe_power(lv, rv);
break;
case LShift:
newval = safe_lshift(lv, rv);
break;
case RShift:
newval = PyNumber_Rshift(lv, rv);
break;
case BitOr:
newval = PyNumber_Or(lv, rv);
break;
case BitXor:
newval = PyNumber_Xor(lv, rv);
break;
case BitAnd:
newval = PyNumber_And(lv, rv);
break;
default: // Unknown operator
return 1;
}
return make_const(node, newval, arena);
}
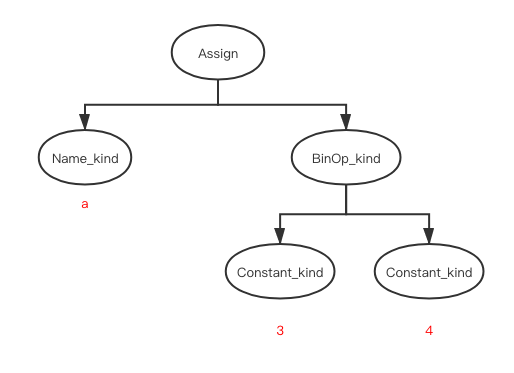
比如
a = 3 + 4
AST 表示如下
在 fold_binop 之后, 变成了
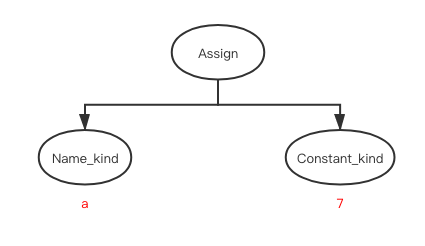
这个常量折叠的方法同样会做如下操作
-
展开二元操作(如上图)
-
展开一元操作(
not/is/isnot) - 把你的手写 list 转换成 tuple
- 展开常量可迭代对象的常量下标
[] - 等待 …
symtable
在 _PyAST_Optimize 之后, PySymtable_BuildObject 会遍历 AST 并把 function/class/name 等定义/声明的变量加到一个 Python 字典对象中

CodeObject
compiler_mod 会遍历这个 AST, 并且生成对应的指令集和所需要的数据, 之后生成对应的 PyCodeObject 对象
static int
compiler_visit_expr1(struct compiler *c, expr_ty e)
{
// ...
case Constant_kind:
ADDOP_LOAD_CONST(c, e->v.Constant.value);
break;
// ...
}
static int
compiler_addop_load_const(struct compiler *c, PyObject *o)
{
// 把对应的常量加到字典对象 c->u->u_consts 中, 并把对应常量的最后的位移位置返回
Py_ssize_t arg = compiler_add_const(c, o);
if (arg < 0)
return 0;
// 把 `LOAD_CONST arg` 加到下一个指令中
return compiler_addop_i(c, LOAD_CONST, arg);
}
// 下列的函数在 Python/compile.c 中可以找到
static int
compiler_addop_i(struct compiler *c, int opcode, Py_ssize_t oparg)
{
struct instr *i;
int off;
// ...
off = compiler_next_instr(c, c->u->u_curblock);
if (off < 0)
return 0;
i = &c->u->u_curblock->b_instr[off];
i->i_opcode = opcode;
i->i_oparg = Py_SAFE_DOWNCAST(oparg, Py_ssize_t, int);
compiler_set_lineno(c, off);
return 1;
}
static Py_ssize_t
compiler_add_const(struct compiler *c, PyObject *o)
{
PyObject *key = merge_consts_recursive(c, o);
if (key == NULL) {
return -1;
}
Py_ssize_t arg = compiler_add_o(c, c->u->u_consts, key);
Py_DECREF(key);
return arg;
}
static Py_ssize_t
compiler_add_o(struct compiler *c, PyObject *dict, PyObject *o)
{
PyObject *v;
Py_ssize_t arg;
v = PyDict_GetItemWithError(dict, o);
if (!v) {
if (PyErr_Occurred()) {
return -1;
}
arg = PyDict_GET_SIZE(dict);
v = PyLong_FromSsize_t(arg);
if (!v) {
return -1;
}
if (PyDict_SetItem(dict, o, v) < 0) {
Py_DECREF(v);
return -1;
}
Py_DECREF(v);
}
else
arg = PyLong_AsLong(v);
return arg;
}
常量在上述操作时是以字典形式存储的, {'a': 0} 键表示对应常量的 PyObject, 值表示参数位移
它最终会被 Python/compile.c->consts_dict_keys_inorder 这个函数按照值里的位移顺序被转换成对应的列表对象,
最终, Python/compile.c->makecode 会把上述的指令和对应的数据结构存储到新建的 PyCodeObject 上
1 0 LOAD_CONST 0 (7)
2 STORE_NAME 0 (a)
4 LOAD_CONST 1 (None)
6 RETURN_VALUE